Medium density fiberboards are an engineered produce made from wood. An MDF board is often compared to plywood boards. However, these two are quite different and most medium density fiberboards are denser than the plywood boards.
Table of Contents
Assets of Medium Density Fiberboards
- Unlike natural wood, an MDF board does not contain rings or knots. This makes the boards much more uniform than their natural counterparts during the process of cutting.
- A typical MDF board has a hard and smooth surface which is completely flat. Moreover, resin and wax are used as binders to make the board strong. This makes the boards perfectly suitable for veneering processes.
- Some of these boards have a uniform density from one end to another of the panel.
These boards can be used in different ways without any problems whatsoever. They can be glued together. Lamination and dowelling can be performed on these boards without any problems whatsoever. The typical types of fasteners used for such boards are pan-head machine screws and T-nuts. Smooth-shank nails cannot be used for these boards, especially near the edges. Fine-pitch screws cannot be used either. These boards are similar to natural wood ones in one respect. Both of them tend to split when the installation of woodscrews is performed with the pilot holes.
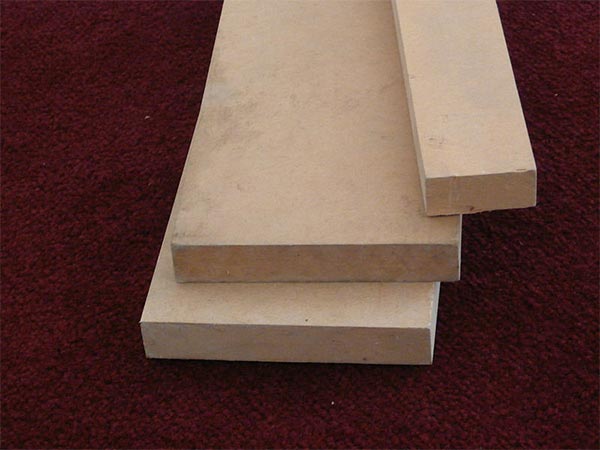 Image From Wikimedia Commons
Image From Wikimedia Commons
Advantages of Medium Density Fiberboards
- A MDF board can be a good substrate for veneers.
- Most of these boards are available quite cheaply. They tend to be cheaper than most natural woods.
- These boards have isotropic properties. In other words, the entire panel will have the same properties. This is due to the absence of grain.
- The wood here does not split.
- Medium density fiberboards are consistent when it comes to their sizes and strength as they are engineered.
- These boards are flexible enough to be used on curved surfaces.
- Medium density fiberboards can be molded into any shapes.
- The dimensions of the boards are stable. They do not contract or expand like natural wood.
- These boards are also moisture and fire-resistant. But that goes well only for the high quality ones.
Disadvantages of Medium Density Fiberboards
- The resins of medium density fiberboards are heavy. This makes them denser than chipboards and plywood.
- Poor quality medium density fiberboards tend to swell when they get saturated with moisture and then break.
- Sealing is crucial as the boards may possibly expand or warp otherwise.
- Medium density fiberboards tend to contain a chemical called urea-formaldehyde. This is a probable carcinogen. It can cause a variety of health risks such as lung and eye irritations and allergies when the boards are being cut or sanded.
- The wood has a tendency to shrink significantly when used in environments that possess a lowered humidity.
Safety Concerns with Medium Density Fiberboards
A MDF board can possess significant safety risks when it is used incorrectly. During the cutting process, these boards tend to release a significant amount of dust which can lead to respiratory problems. Additionally, the exposed edges must be sealed. This ensures that the emissions are limited.
The resins used to bind the fibers together in a medium density fiberboard are made from formaldehyde. This formaldehyde is constantly released freely by the boards. There are other volatile organic compounds which are released together. These compounds tend to pose significant health risks as the concentrations in the emissions are considered to be unsafe. Coating will be necessary after completing the work to ensure that the free formaldehyde has been sealed in.
Medium density fiberboards can be extremely helpful in many cases where natural wood is unsuitable. However, care must be taken when it comes to their use as it can be extremely harmful otherwise. Still want you know more things? Then please go here and get more info about MDF Board.









Leave a Reply